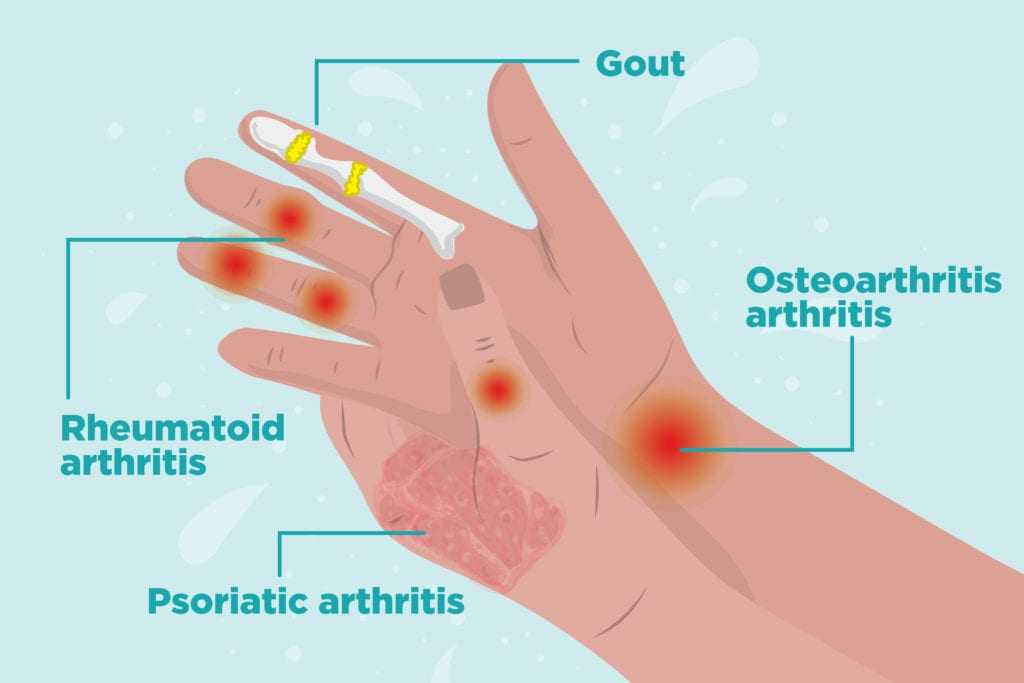
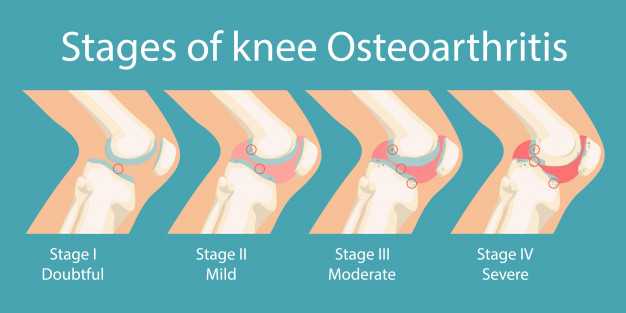
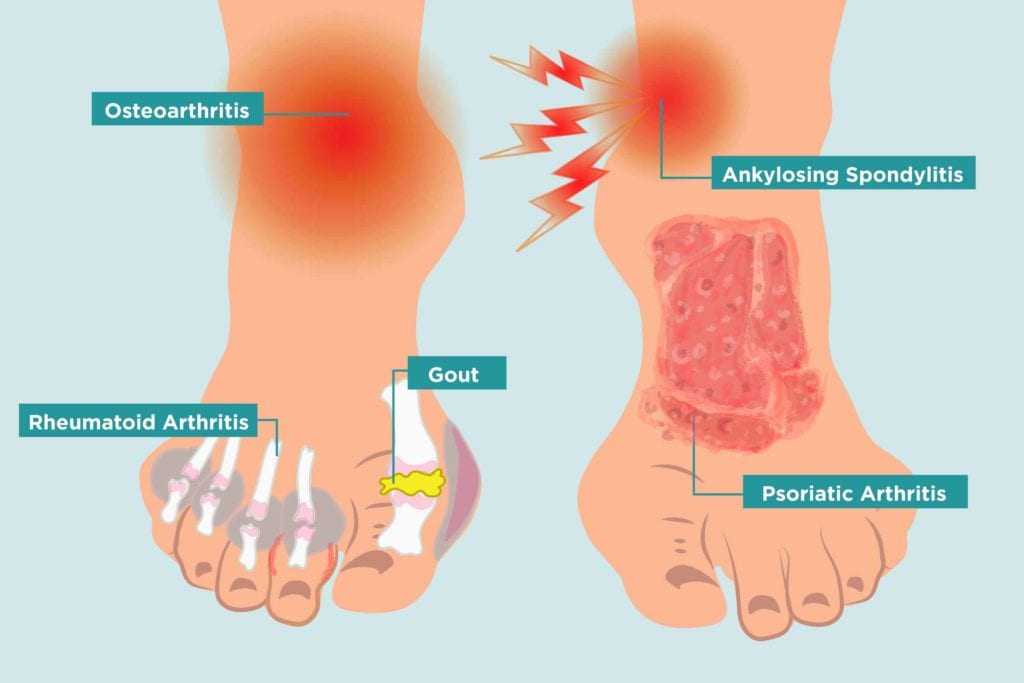
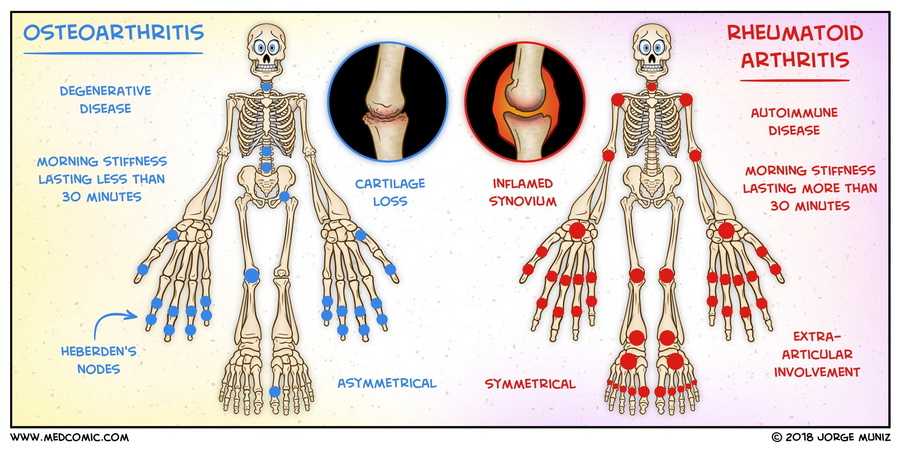
What does Joint Cartilage have in common with Potholes?
A good analogy of joint pain is that the cartilage between your joints is like a road with potholes. The roadway starts off perfect. Over time, with wear and tear, it gets small potholes and cracks. We think our joints are perfectly fine, but actually, the car tyres are crossing over those small potholes. We don’t have pain and we are hopeful this will continue into old age.
But at some stage, and mostly unexpectedly, the potholes get so big, the car tyres cannot bridge those widening potholes and the car ride now is extremely bumpy. And painful. And no or very reduced mobility. Surgery fixes the potholes or puts in a whole new road!
Joint decline is not a straight line but most often is progressive and comes on suddenly but sometimes briefly (technically called episodic acute). It generally gets worse as the deterioration continues. Pain is not from the cartilage, but nerves that are in the bones and soft tissues (e.g. capsules, and ligaments) around the joint. Damaged cartilage itself is relatively pain insensitive. The experience of pain from damaged and degenerating joints varies widely. Pain does not affect everyone the same way. Tests with X-rays and MRI scans don’t always correlate with pain or disability. The nervous system varies between people. Some have insensitive nervous symptoms and say they have little pain. Others are labeled as having a low pain threshold. We may say someone is “stoic” but it may just be they don’t have a sensitive nervous system. And pain may not be in the joint, but might be in an area well away from the joint itself.
It is estimated the correlation between pain and measurable damage is about 65% and physiotherapists will talk about a skeletal age versus organic aging.
Degradation Curve of Joint Pain
At some stage, joints start to decline. We don’t notice for a long time but by mid thirties to mid fifties we notice aches and pains.
In our earlier years, most have healthy joints. Children have breaks, sprains, but most heal.
We will consider important factors including early diagnosis, prevention, delay and cure.
By the 50’s we are contemplating surgery. By the 70’s we are filling up hospital surgeries. This does not include the cohort who suffer damage at 15 years of age, have surgery at 25, more surgery at 35 and by 45 are surgical curiosities!
Osteoarthritis Costs You Dearly
OA costs you money. As a consequence of symptoms and activity limitations, OA leads to medical costs and costs due to productivity loss of over $1,000 per patient per month, twice as much as other chronic diseases such as diabetes (Hermans et al. 2012)
3 Options to Reduce Joint Pain
In the figure above, we really only have 3 options to reduce joint pain.
- 1- Prevent
- 2 – Delay
- 3 – Cure
- Prevent joints declining. What are the things to do so that our joints are in good shape until we die? Taking pain killers for years is not prevention. It stops the pain but does nothing in terms of the physical damage that is occurring in the joints.
- Delay – can you delay by 10 or 20 years with recommended lifestyle changes – remaining in the green zone of healthy joints, or at worse in the yellow zone, but with minor pain?
- Cure – Not everyone has the money for surgery or other new medical techniques.
1. Prevention – The Best Option
Some joint pain is inevitable. You cannot stop aging. Most physiotherapists & researchers say that the joints of the human body are good for maybe 55 years and then start to suffer measurable degradation. Joints wear out as the cartilage thins, bones reduce in strength. However, joints do not wear out in a straight line fashion. There are lifestyle choices to reduce the rate of wear.
We think of joints as simply bone on bone with a cartilage in between, but it is more complex. The joint capsule consists of two layers, an outer fibrous layer, fibrous capsule, and an inner layer called the synovial membrane. The synovial membrane is a thin, vascular lining that covers the inner surfaces of the joint capsule and intra-articular ligaments and tendons.The lining of the capsule, the synovial membrane makes synovial fluid which provides nutrition and lubrication.
There are multiple causes of joint damage, leading to joint pain. In synovial joints, cartilage separates the two bones. The cartilage can fracture, but it is the other parts of the joint that get inflamed.
Pain receptors are in the bone and the capsules that surround the joint. There are many pain receptors in these structures, but relatively few pain receptors in the cartilage itself. As the bearing surface of the joint (cartilage) wears down, inflammation and pain sets in.
2. Delay – The Next Best 5 Options.
There are 5 Simple Strategies to Delay Joint Pain
- Be Active. The expression is if you don’t use it, you lose it. Walk 2 to 3 km per day, or swim, or do low impact exercises such as yoga or pilates. Low impact, consistent movement maintains not just joint health but overall health. One study showed walking more than 1 hour per day meant their medical care was $100,000 less over their lifetime and extended their life for 2 years. (Nagai et al. 2011) Adopting the popular High Intensity Technique (HIT exercise) will cause severe joint pain unless you spend months (or even up to 1 year if you are very deconditioned) getting the knees and joints strong enough to take that HIT energy. HIT is great for cardiovascular improvement but without preparation is also good for physiotherapists billing.
- Avoid employment that has heavy lifting or kneeling if you want to minimise OA (Ezzat and Li 2014)
- Avoid foods that cause inflammation and arthritis. There is lots of data recently that inflammation is a cause of arthritis (Kim et al. 2013) Excess added sugar is probably the primary cause of inflammation. Your diet should avoid sugar sweetened cereal, snack bars, pre-sweetened dairy products, canned fruit and condiments, particularly ketchup, BBQ sauce, honey mustard, French dressing, and similar. Do not eat any food that is more than 3% added sugar. The WHO recommendation is for less than 5% of diet or 25 grams (6 teaspoons) of added sugar in your diet per day! Purchase food from around the outside of the supermarket – fresh or frozen whole food. Avoid any centre isles. Alcohol consumption has not been reported as a cause! (Karlson et al. 2003) although excess consumption in animals is inflammatory. (Kc et al. 2015)
- Manage your weight. If you become overweight or obese with metabolic symdrome, evidenced by elevated blood pressure, elevated blood glucose levels, increased waist measure and elevated lipids then 75% will have joint pain, versus 25% if you are not. (3 times more). Obesity is a sign of an inflammatory diet. A study that looked at heavy physical work confirmed kneeling or squatting, heavy lifting and arm elevation did get about 30% more arthritis, but those with higher body mass, had higher rates of arthritis (Brennan-Olsen et al. 2018)
- Consume anti-inflammatory foods. In a Nature paper on animal joints (Sekar et al. 2017), the addition of anti-inflammatory foods increased the amount of cartilage. When the animals ate an inflammatory diet which included long chain fatty acids, the animals got metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis symptoms. When they ate antiflammatory materials, they did not get metabolic syndrome and their cartilage improved!.
3. Is there a Silver Bullet for causes of Joint Pain?
There is no 100% certainty of “cure” for joint pain, especially when there has been a history of major joint trauma. There are livestyle changes that can reduce pain and allow people to live with pain if it is not too severe. But people are often left on waiting lists.. If they have money or public health they will be able to get surgery. The typical “conservative” surgery is a technique that Germany calls “re-surfacing” where some of the wear parts are resurfaced, not replaced. The joints are complex, and often the ligaments and soft tissue remains, and may cause subsequent pain. Surgery has its own health risks and is often oversold as a cure. In UK, about 16% of women, 8% of men over 80 have had hip resurfacing or replacements. Surgery is not an absolute cure for joint pain, although with greater than 95% of patients experiencing significant but variable relief from hip pain. Experts disagree what constitutes “success” – pain, movement. The success rate of hip “replacements” 10 years after surgery has been optimistically measured at 90- 95% but at 20 years is down to 80-85%. Some unfortunately experience as much pain after surgery as before.
Seaweed Reduces Joint Pain
Hundreds of customers have told us eating seaweed has reduced their joint pain. Some tell us that it has made no difference.
We suspect the improvement depends one where you are on this joint degradation curve, genetics, diet, and what specifically is wrong.
What Do the Experts Say
The CDC of USA (“5 Proven Ways to Manage Arthritis | CDC” 2019) says there are 5 Proven Ways to minimise Joint Pain.
- Learn new self-management skills.
- Be active.
- Talk to your doctor.
- Manage your weight.
- Protect your joints.
Why do they recommend talking to your doctor? With over 104 different types of arthritis, it is important to know which type you have. Is there a genetic cause? Have you played competitive sports or injured joints? Are there other joint issues? There are genetic causes and there are other techniques and strategies for treatments. Their focus will be to reduce pain, minimize joint damage and improve or maintain function and quality of life. They can also assist with other chronic conditions, like diabetes or heart disease.
Note that in Europe and UK, you are likely to be referred to an inflammatory specialist, who will look at a range of conservative treatments, and who may then refer you to an orthopedic surgeon. In contrast, in USA or Australia you are likely to be directly referred to an orthopedic surgeon.
Joint Pain – You are Not Alone
Joint pain (osteoarthritis or OA) is serious, and getting worse. The numbers are staggering. A recent report (Cui et al. 2020) looking at 10 million people says over 16% for those aged 15. It increases to 23% for those aged 40, and close to 70% if over 60. That’s over 600 million people aged over 40 years in 2020 worldwide. As people age, it gets worse. For elderly of 85+, in UK (Duncan et al. 2011) 65% had joint pain and women had more pain (69%) than men (58%)
Some say that humans have a joint life of about 55 years. After that we are “the walking wounded”. But we also know joint pain is worse for anyone who does the high risk physical sports as explained below.
Damage to Joints from High Impact Sports
Previously we have talked about the need to protect your joints from damage from an early age. Competitive sports that have sudden changes of direction, particularly in spiked shoes and with body contact are demonstrably higher risk and have long term consequences.(Short and Tuttle 2020)
People who do high performance sports activities with rapid change of direction are the most susceptible. Gymnasts , footballers, basketballers who play competitive sports into their 20’s or 30’s have between 5 to 20 times more surgery. (Vogel et al. 2011)
A surprising number of knee and hip joints are replaced each year and it has been known for decades that high impact sports are a major contributor to joint pain. Sports identified as high risk include::
- Gymnastics – where the gymnast is coming down at speed onto mats or floors. Tennis also has rapid change of movement.
- Football – whether soccer, Rugby League (Gibbs 1994), Union, or American football.(Song et al. 2019; Gouttebarge, Aoki, and Kerkhoffs 2018). Those sports with spiked shoes and contact are the worst, so soccer is less risky than league or rugby which have both spiked shoes and body contact.
- Playing competitive sports past mid 20’s.
The increase can be hundreds of times higher than the normal population. The sports bodies have been reluctant to admit the potential for injury. (Khan et al. 2019) In 2018 (Gouttebarge, Aoki, and Kerkhoffs 2018) showed current and retired professional footballers were nearly twice as likely to suffer from knee OA by every additional severe knee injury and by every additional knee surgery they they incurred during their career.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Damage Increases OA
Cruciate ligaments are found inside your knee joint. They cross each other to form an “X” with the anterior cruciate ligament in front and the posterior cruciate ligament in back. The cruciate ligaments control the back and forth motion of your knee.
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) runs diagonally in the middle of the knee. It prevents the tibia from sliding out in front of the femur, as well as provides rotational stability to the knee. ACL damage is becoming more common. The damage when you do an ACL may not be just to the ligaments and surrounding tissue and ligaments. The damage may be more substantial.
Those who do an ACL, will almost certainly have osteoarthritis later in life. (Khan et al. 2019). A recent trend has seen a doubling of ACL injury in younger adults – which is thought to be a result of social drive to have young adults excel in sports (Zbrojkiewicz, Vertullo, and Grayson 2018). This will inevitably give rise to more OA in the next decades
.
Bone Bruising and Osteoarthritis Dissecans
Another cause of osteoarthritis is caused by bone bruising. ACL injuries may also occur in conjunction with bone bruising. Sometimes sports people will suffer an ACL but also have OA dissecans, fix the ACL but still have ongoing bone bruising (Bredella et al. 2000)
A typical cause of this injury used to be in the military where soldiers would jump off trucks with a fully laden pack, and wonder 15 years later why all the soldiers needed knee operations. Fortunately they followed the science. It also happens with people such as high jumpers or long jumpers.
During rapid stopping, or during an ACL injury event, the scrunched bones in the joint get a “bone bruise”. The “bone bruise” is actually a fracture, results in a chalky area, and then repeated exercise opens up a hollow space in the bone. You get chronic inflammation from the irritation of the lining on the joint (the synovium) and it causes an increase of cells producing inflammatory fluid. It is called reactive synovitis or “water on the knee”.
Filling this hollow space with a lubricant (reactive synovitis) has gone out of favour but with good slow rehabilitation the risk of subsequent OA is reduced.
Cartilage – Not All the Same
Joints are complex. While babies start with 270 joints we have 206 named joints but with the inclusion of sesamoids which are are bones imbedded in tendons, but not connected to other bones. The patella (kneecap) is the largest sesamoid. These bones vary in number from person to person. So generally we have between 250 and 350 joints. (Barbe et al. 2009). Major joints – knee, ankle, elbows, wrists and shoulders are over-represented for pain.
We think about bone, and cartilage and while the bones have the nerves, the cartilage keeps the bones apart and moving freely. There are different types of cartilage. And the layers that produce the cartilage are different. Technically, cartilage is classified as a special connective tissue with mesodermal origin characterised by a cellular component immersed within ECM composed of ground substance (polysaccharides), a fibrillar component (fibrous proteins), and interstitial fluid (mainly water). There is no direct supply of blood, lymphatics and nerves; nutrition relies on diffusion from the surrounding tissues. Based on the composition and function, it is possible to distinguish three types of cartilaginous tissues: hyaline, fibro- and elastic cartilage.(Armiento, Alini, and Stoddart 2019). With that complex of various bone, cartilage and connective tissue, specific identification and causes of pain can be difficult.
Early Diagnosis & Causes of joint pain
A key part of AO treatment is early and proper diagnosis. The complexity of OA means that for many wrong diagnoses means incorrect treatment. The absence or presence of pain is a poor measure. When you consider a joint has a whole raft of connective tissue, cartilage, bones, synovial fluid, synovial tissue and OA may be identified as inflammation in other joints. There are various tests the physiotherapist/doctor/rheumatologist or orthopedic surgeon will do but there are also tests that have not been developed or identified yet.
The research by Prof Lindsay Brown and Prof Xiao say that restoration of cartilage and synovial membrane can be increased with anti-inflammatory functional food including seaweed. But if the damage from previous injuries is severe, restoration may take a longer time. Given there are 360 joints in the human body, any reduction in inflammation is welcome!
More Reading
Thanks to Greg Sheather (ret), Muscular Physiotherapist, Dip Phy Grad Dip Manipulative Therapy (Sydney) for the analogy of the potholes.
“5 Proven Ways to Manage Arthritis | CDC.” 2019. February 5, 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/management.htm.
Armiento, Angela R., Mauro Alini, and Martin J. Stoddart. 2019. “Articular Fibrocartilage – Why Does Hyaline Cartilage Fail to Repair?” Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, Wound healing and fibrosis – State of play, 146 (June): 289–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2018.12.015.
Barbe, Mary, Jeffrey Driban, Ann Barr, Steven Popoff, and Fayez Safadi. 2009. “Structure and Function of Joints.” In Bone Pathology, 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-347-9_2.
Bredella, M. A., P. F. Tirman, T. K. Wischer, J. Belzer, A. Taylor, and H. K. Genant. 2000. “Reactive Synovitis of the Knee Joint: MR Imaging Appearance with Arthroscopic Correlation.” Skeletal Radiology 29 (10): 577–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002560000259.
Brennan-Olsen, Sharon L., Svetlana Solovieva, Eira Viikari-Juntura, Ilana N. Ackerman, Steven J. Bowe, Paul Kowal, Nirmala Naidoo, et al. 2018. “Arthritis Diagnosis and Symptoms Are Positively Associated with Specific Physical Job Exposures in Lower- and Middle-Income Countries: Cross-Sectional Results from the World Health Organization’s Study on Global AGEing and Adult Health (SAGE).” BMC Public Health 18 (June). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5631-2.
Cui, Aiyong, Huizi Li, Dawei Wang, Junlong Zhong, Yufeng Chen, and Huading Lu. 2020. “Global, Regional Prevalence, Incidence and Risk Factors of Knee Osteoarthritis in Population-Based Studies.” EClinicalMedicine 29–30 (December): 100587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100587.
Duncan, Rachel, Roger M. Francis, Joanna Collerton, Karen Davies, Carol Jagger, Andrew Kingston, Tom Kirkwood, Louise Robinson, and Fraser Birrell. 2011. “Prevalence of Arthritis and Joint Pain in the Oldest Old: Findings from the Newcastle 85+ Study.” Age and Ageing 40 (6): 752–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afr105.
Ezzat, Allison M., and Linda C. Li. 2014. “Occupational Physical Loading Tasks and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of the Evidence.” Physiotherapy Canada. Physiotherapie Canada 66 (1): 91–107. https://doi.org/10.3138/ptc.2012-45BC.
Gibbs, Nathan. 1994. “Common Rugby League Injuries.” Sports Medicine 18 (6): 438–50. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199418060-00007.
Gouttebarge, Vincent, Haruhito Aoki, and Gino M. M. J. Kerkhoffs. 2018. “Knee Osteoarthritis in Professional Football Is Related to Severe Knee Injury and Knee Surgery.” Injury Epidemiology 5 (1): 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40621-018-0157-8.
Hermans, Job, Marc A. Koopmanschap, Sita M. A. Bierma-Zeinstra, Joost H. van Linge, Jan A. N. Verhaar, Max Reijman, and Alex Burdorf. 2012. “Productivity Costs and Medical Costs among Working Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis.” Arthritis Care & Research 64 (6): 853–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.21617.
Karlson, Elizabeth W, Lisa A Mandl, Gideon N Aweh, Oliver Sangha, Matthew H Liang, and Francine Grodstein. 2003. “Total Hip Replacement Due to Osteoarthritis: The Importance of Age, Obesity, and Other Modifiable Risk Factors.” The American Journal of Medicine 114 (2): 93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9343(02)01447-X.
Kc, Ranjan, Robin Voigt, Michael B Ellman, Xin Li, Keith C. Summa, Christopher B Forsyth, Ali Keshavarzian, Fred W. Turek, Jae-Sung Kim, and Hee-Jeong Im. 2015. “Chronic Alcohol Consumption Induces Osteoarthritis-Like Pathological Changes in an Experimental Mouse Model.” Arthritis & Rheumatology (Hoboken, N.J.) 67 (6): 1678–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39090.
Khan, Tanvir, Abtin Alvand, Daniel Prieto-Alhambra, David J. Culliford, Andrew Judge, William F. Jackson, Brigitte E. Scammell, Nigel K. Arden, and Andrew James Price. 2019. “ACL and Meniscal Injuries Increase the Risk of Primary Total Knee Replacement for Osteoarthritis: A Matched Case-Control Study Using the Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD).” British Journal of Sports Medicine 53 (15): 965–68. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-097762.
Kim, Jae-Sung, Michael B. Ellman, Dongyao Yan, Howard S. An, Ranjan Kc, Xin Li, Di Chen, et al. 2013. “Lactoferricin Mediates Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Catabolic Effects via Inhibition of IL-1 and LPS Activity in the Intervertebral Disc.” Journal of Cellular Physiology 228 (9): 1884–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24350.
Nagai, Masato, Shinichi Kuriyama, Masako Kakizaki, Kaori Ohmori-Matsuda, Toshimasa Sone, Atsushi Hozawa, Miyuki Kawado, Shuji Hashimoto, and Ichiro Tsuji. 2011. “Impact of Walking on Life Expectancy and Lifetime Medical Expenditure: The Ohsaki Cohort Study.” BMJ Open 1 (2): bmjopen. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000240.
Sekar, Sunderajhan, Siti Raihanah Shafie, Indira Prasadam, Ross Crawford, Sunil K. Panchal, Lindsay Brown, and Yin Xiao. 2017. “Saturated Fatty Acids Induce Development of Both Metabolic Syndrome and Osteoarthritis in Rats.” Scientific Reports 7 (46457): 11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46457.
Short, Steven, and Matthew Tuttle. 2020. “THE GAP BETWEEN RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE FOR INJURY PREVENTION IN ELITE SPORT: A CLINICAL COMMENTARY.” International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy 15 (6): 1229–34. https://doi.org/10.26603/ijspt20201229.
Song, Kyeongtak, Erik A. Wikstrom, Joshua N. Tennant, Kevin M. Guskiewicz, Stephen W. Marshall, and Zachary Y. Kerr. 2019. “Osteoarthritis Prevalence in Retired National Football League Players With a History of Ankle Injuries and Surgery.” Journal of Athletic Training 54 (11): 1165–70. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-421-18.
Vogel, Laura A., Giuseppe Carotenuto, John J. Basti, and William N. Levine. 2011. “Physical Activity After Total Joint Arthroplasty.” Sports Health 3 (5): 441–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941738111415826.
Zbrojkiewicz, David, Christopher Vertullo, and Jane E. Grayson. 2018. “Increasing Rates of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in Young Australians, 2000–2015.” Medical Journal of Australia 208 (8). https://www.mja.com.au/journal/2018/208/8/increasing-rates-anterior-cruciate-ligament-reconstruction-young-australians.